TAPro User Guide

TAPro is your go-to Contact Book, created with love for Computer Science Teaching Assistants (TAs) like you. We get it — juggling your students and keeping track of attendance can be a handful. That’s why TAPro is here to make your life easier. With features designed precisely for you, it's all about simplifying those time-consuming tasks, letting you focus on what you do best: teaching and inspiring your students. Welcome to a smoother, more personalized way of managing your TA duties!
TAPro is optimized for use via a Command Line Interface (CLI) while still having the benefits of a Graphical User Interface (GUI).
If you can type fast, TAPro can get your contact management and attendance taking tasks done faster 🚀 than traditional GUI apps.
Table of Contents
- Navigating this User Guide
- Useful Notations and Glossary
- Navigating the GUI
- Quick start
- Features
- Viewing help:
help - Name/Rename CS course:
setcrs - Adding a student:
addstu - Listing all students:
list - Editing a student:
edit - Locating students by name:
find - Marking a student's attendance for a given week by their NUSNet ID:
mark - Unmarking a student's attendance for a given week by their NUSNet ID:
unmark - Deleting a student:
delstu - Clearing all entries:
clear - Exiting the program:
exit - Autocomplete
- Retrieving command history
- Saving the data
- Editing the data file
- Viewing help:
- Command summary
- Known issues
- FAQ
Navigating this User Guide
Welcome to the cozy corner of the TAPro User Guide! 🌟 Whether you're embarking on your very first day as a TA or you're practically a wizard with student info, we've put together this guide to make sure you get the most out of TAPro.
New around here? No worries, we've got you. Start with these sections to become a TAPro buddy in no time:
- Useful Notations and Glossary: Familiarize yourself with the terms and symbols used throughout this guide.
- Navigating the GUI: Visually learn to navigate around the command box and those handy contact cards.
- Features: Dive into the exciting world of features we've brewed up just for you.
Ready to Roll? Skip over to Quick Start for the no-fuss, easy-peasy steps to download TAPro and get ready for action.
🚀 Already a TAPro champ? Let's add some spice to your TA skills:
- Set Course: Tailor TAPro to your current course with
setcrs. - Add Student: Got a new face in class? Quickly add their details with
addstu. - Mark: Keep track of weekly attendance with
mark. - Unmark: Oops, made a mistake?
unmarkreverses that mark. - List: Bring up a complete list of your students with
list. - Edit: Update details as they evolve with
edit. - Find: Looking for someone?
findhelps you search by keyword. - Delete Student: Time to say goodbye? Remove a student from your list with
delstu. - Clear: Need to wipe the slate clean?
cleardoes just that.
Need a quick TAPro refresher? Our Command Summary is like the TAPro bible—short, sweet, and to the point.
Stumbled upon a hurdle or just curious? Swing by our FAQ where we tackle all your burning questions and offer nuggets of wisdom for a smooth TAPro journey.
Useful Notations and Glossary
This segment aims to make your TAPro experience as smooth as silk. With these notions and terms at your fingertips, you're well on your way to becoming a TAPro power user!
Diving into TAPro, you'll encounter some handy notations and terms. We've decoded them here to make your journey smoother and more enjoyable.
Symbols
Symbols are indicators that give additional information about a target piece of text.
| Symbol | Meaning of target text |
|---|---|
| Tip | |
| Warning | |
| Important | |
| Additional useful information | |
| Valid example | |
| Invalid example | |
| Danger | |
| Definition | |
| Question | |
| Command Format | |
| KEY | Keyboard key input |
syntax | Input and output related syntax |
| link | Clickable link |
Keywords
Keywords are word(s) that hold greater significance.
| Keywords | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Attribute | A single detail of a student. |
| Autocomplete | A feature that predicts and completes commands as you type. |
| Autocompletion | The autocomplete feature's suggested result(s). |
| Command | An executable input text in the command input box. |
| Command History | A record of successfully executed commands that can be retrieved for reuse. |
| Command Line Interface | A text-based interface used for entering commands directly. |
| Command Name | The word used to identify that it's associated command is used. |
| Graphical User Interface | The visual interface that enhances user interaction with graphical elements. |
| Parameter | A piece of information can be used in commands to be executed. |
| Placeholder Value | A parameter value used to indicate that a value is not set for an attribute. |
| Recognized Prefix | A prefix that has an associated parameter and attribute. |
Abbreviations
Abbreviations are a shortened form of a word or phrase.
| Abbreviation | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ASCII | American Standard Code for Information Interchange |
| CLI | Command Line Interface |
| CS | Computer Science |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| JSON | JavaScript Object Notation |
| NUS | National University of Singapore |
| TA | Teaching Assistant |
| UI | User Interface |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
Command Format
Commands formats have specific notations to represent how a command can be used.
| Notation | Meaning |
|---|---|
prefix/ | Represents a prefix. |
UPPER_CASE | Represents parameters that need to be given by you! |
[ELLIPSIS]... | Indicates that a parameter can be repeated or omitted entirely. |
[SQUARE_BRACKETS] | Denotes optional parameters. |
Prefixes must have a space in front of them.
Parameters and their Recognized Prefixes
Recognized Prefixes: Prefixes that have an associated parameter and attribute in TAPro.
| Parameter | Recognized Prefix | Attribute | Constraints |
|---|---|---|---|
NAME | n/ | Name of the student. | Proper-case and alphabetical characters only. |
NUSNET | nn/ | NUSNet ID of the student. | Case-insensitive, unique identifier. |
PHONE | p/ | Phone number of the student. | At least 3 digits, and digits only. |
EMAIL | e/ | Email address of the student. | Case-insensitive, valid email address. |
MAJOR | m/ | Major of the student. | Unconstrained. |
TAG | t/ | Tag(s) of the student. | Case-sensitive, alphanumeric without spaces. |
WEEK | wk/ | Week number of student's attendance. | Integer between 1 to 13 (inclusive). |
Tags can be associated with a student for categorization.
Other Parameters
These parameters are not associated with an attribute and do not have recognized prefixes.
| Parameter | Meaning |
|---|---|
COURSE_CODE | Course code which the user is tutoring for. |
INDEX | The numbered position of a student in the student contact cards panel. |
KEYWORD | The main search keyword for student names. |
MORE_KEYWORDS | Additional search keywords for student names. |
Navigating the GUI
Welcome to the TAPro GUI! 🎉 Here's a quick tour to help you get comfortable with the interface:
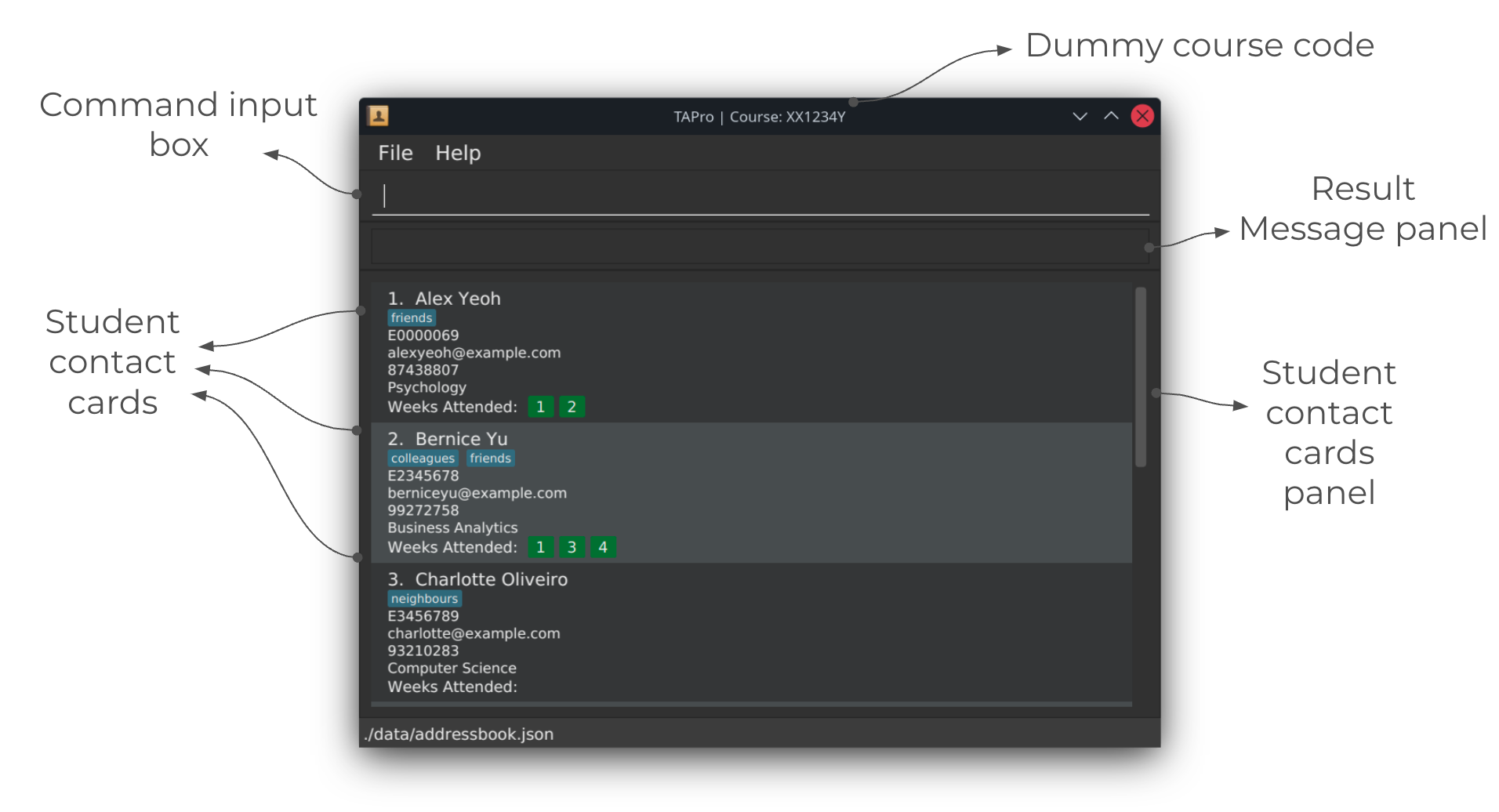
Quick start
- Ensure you have Java 11 or above installed in your computer.
Installing Java:
If you do not have Java 11 or above installed, you can download the latest available version of Java from here.
For macOS users, you may wish to follow the instructions here.
Only Java 11 has been tested to work with TAPro, so check that your Java version is correct if you are facing issues with TAPro.
Download the latest version of
TAPro.jarfrom here.Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your TAPro.
Open a command terminal,
cdinto the folder you downloaded the JAR file in, and run thejava -jar TAPro.jarcommand to launch the application.
A GUI similar to the below image should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
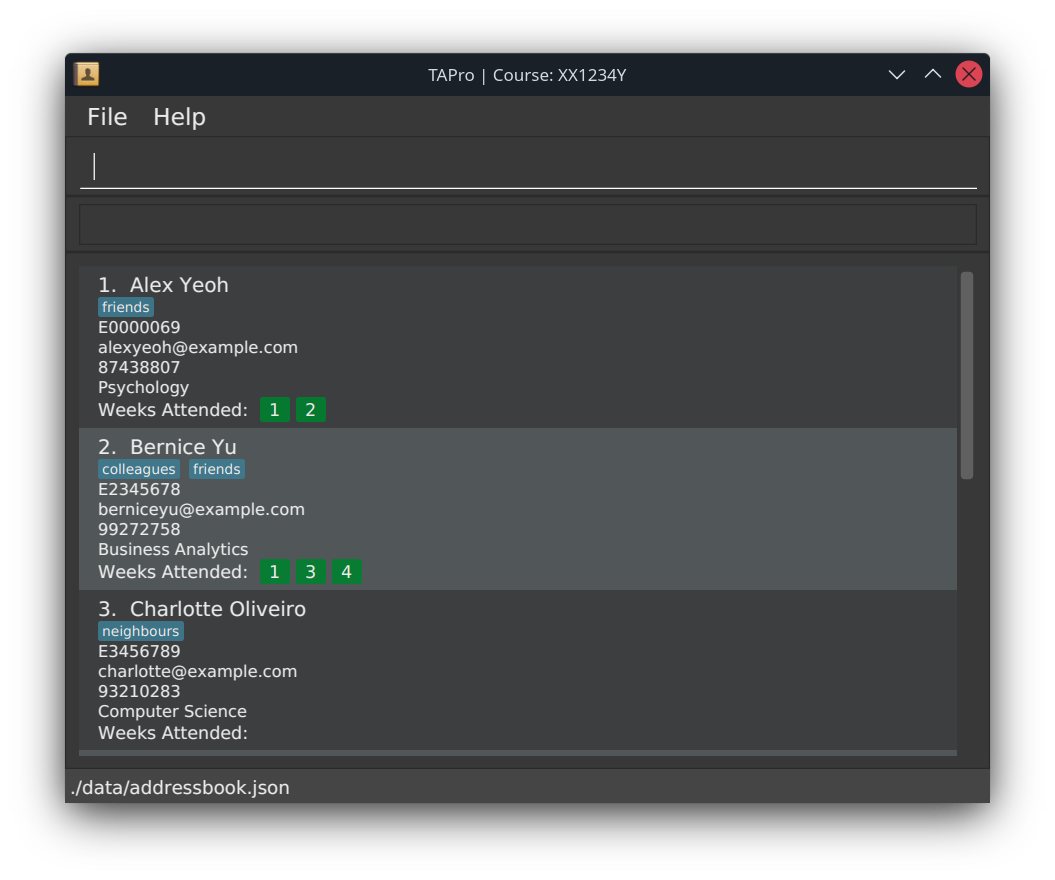
- Type a command in the command input box and press ENTER to execute it.
Example: Typing help in the command input box and pressing ENTER will open the help window.
Here are some example commands you can try:
list: Lists all contacts.addstu nn/E0952224 n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com m/Computer Science: Adds a student namedJohn Doeto the contact book.delstu nn/E0952224: Deletes the student with NUSNet ID E0952224 from the contact book (assuming they were already in the contact book).clear: Deletes all students, and their contact and attendance information.exit: Exits the application.
- Refer to the sections under Features below for details of each command.
Features
About the command format:
Words in UPPER_CASE are the parameters to be supplied by the user.
Example: In addstu n/NAME, NAME is a parameter which can be used as addstu n/John Doe.
Items in square brackets are optional.
Example: n/NAME [t/TAG] can be used as n/John Doe t/friend or as n/John Doe.
Items with … after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
Example: [t/TAG]… can be used as (i.e. 0 times), t/friend, t/friend t/family etc.
Parameters can be in any order.
Example: If the command specifies n/NAME p/PHONE, p/PHONE n/NAME is also acceptable.
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as help, list, exit and clear) will be ignored.
Example: If the command specifies help 123, it will be interpreted as help.
Non-recognized prefixes be parsed as part of the previous parameter's value.
Example: If the command specifies addstu n/John Doe a/Non-recognized-prefix, it would be parsed as NAME parameter being John Doe a/Non-recognized-prefix, instead of just John Doe, as a/ is not a recognized prefix.
When using a PDF version of this document:
Be careful when copying and pasting commands that span multiple lines as space characters surrounding line-breaks may be omitted when copied over to the application.
Viewing help : help
Entering the help command opens a help window that shows a message explaining how to access the help page,
as well as quick reference of each command with simple examples on how to use them.
Format: help
- Additional arguments after
helpwill be simply ignored.
A new window is opened:
A new window is opened, so that it does not clutter up your main window. A GUI similar to the below image should appear.
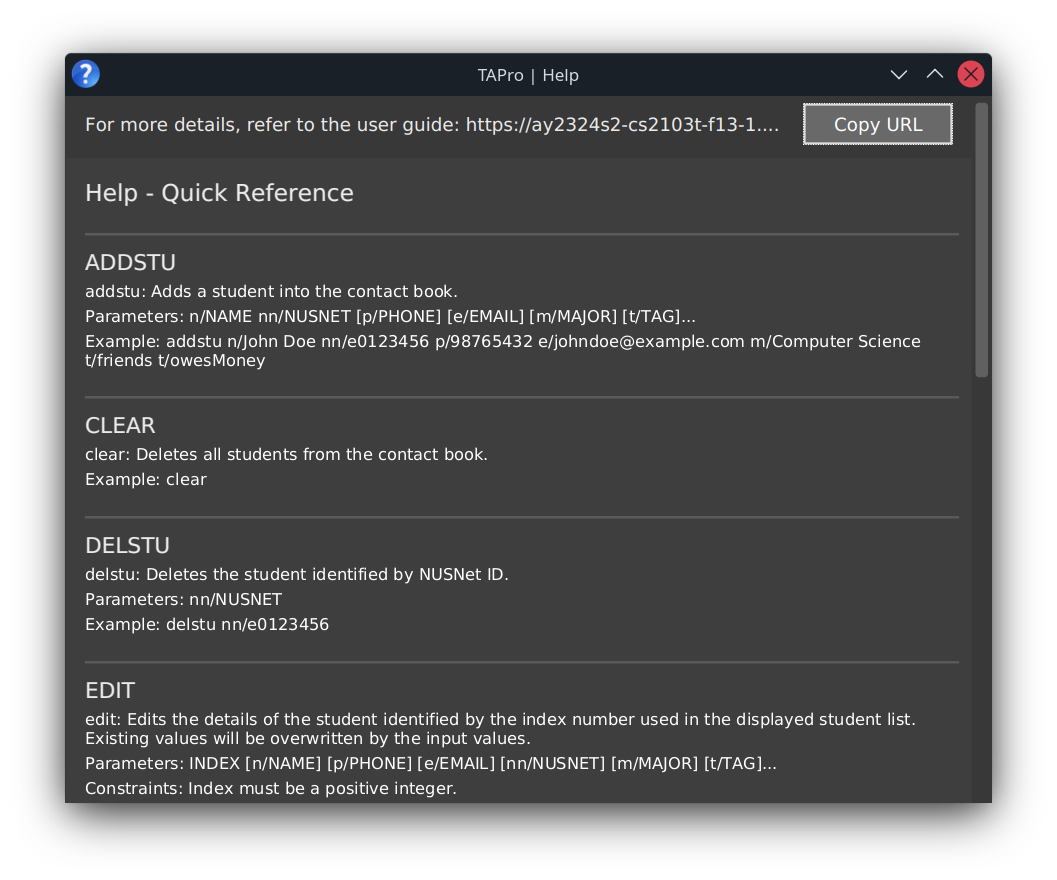
More about help's quick reference:
The quick reference is meant for fast and reliable lookup of commands and their usages, without needing an internet connection and opening a browser to get an overview of the commands.
- It is not meant to contain detailed information about each command. To access detailed information about each command, you can refer to our user guide.
Resizing the help window:
The help window is resizable, so you can easily reposition and resize it to fit anywhere on your screen, exactly where you want it to be.
Switching quickly between the help and main window:
On Windows and most Linux distributions, you can use the keyboard shortcut: ALT + TAB, to switch between windows quickly.
On macOS, you can use the keyboard shortcut: ⌘CMD + `, to switch between windows quickly.
Screenshots of using the help command:
Help window:
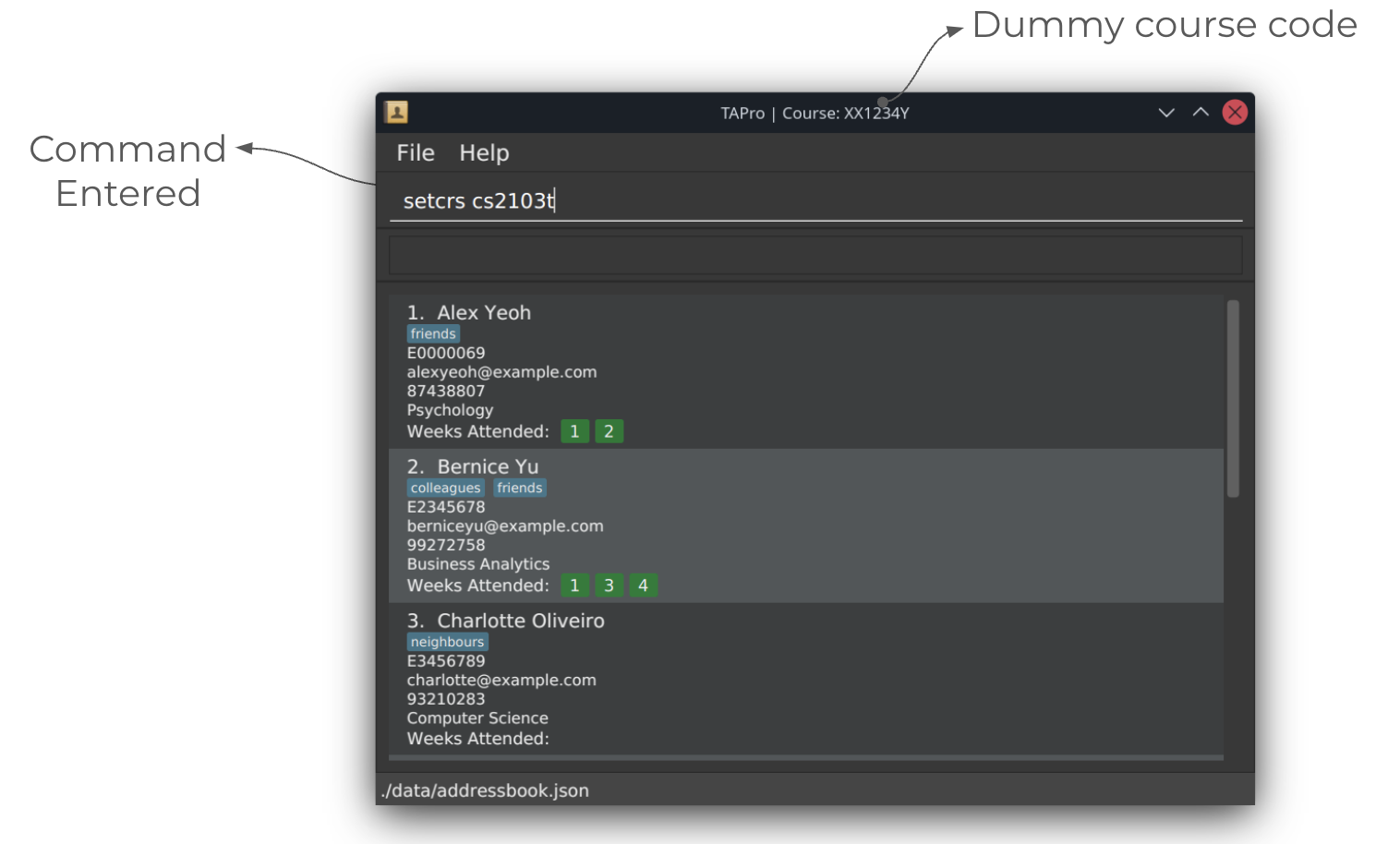
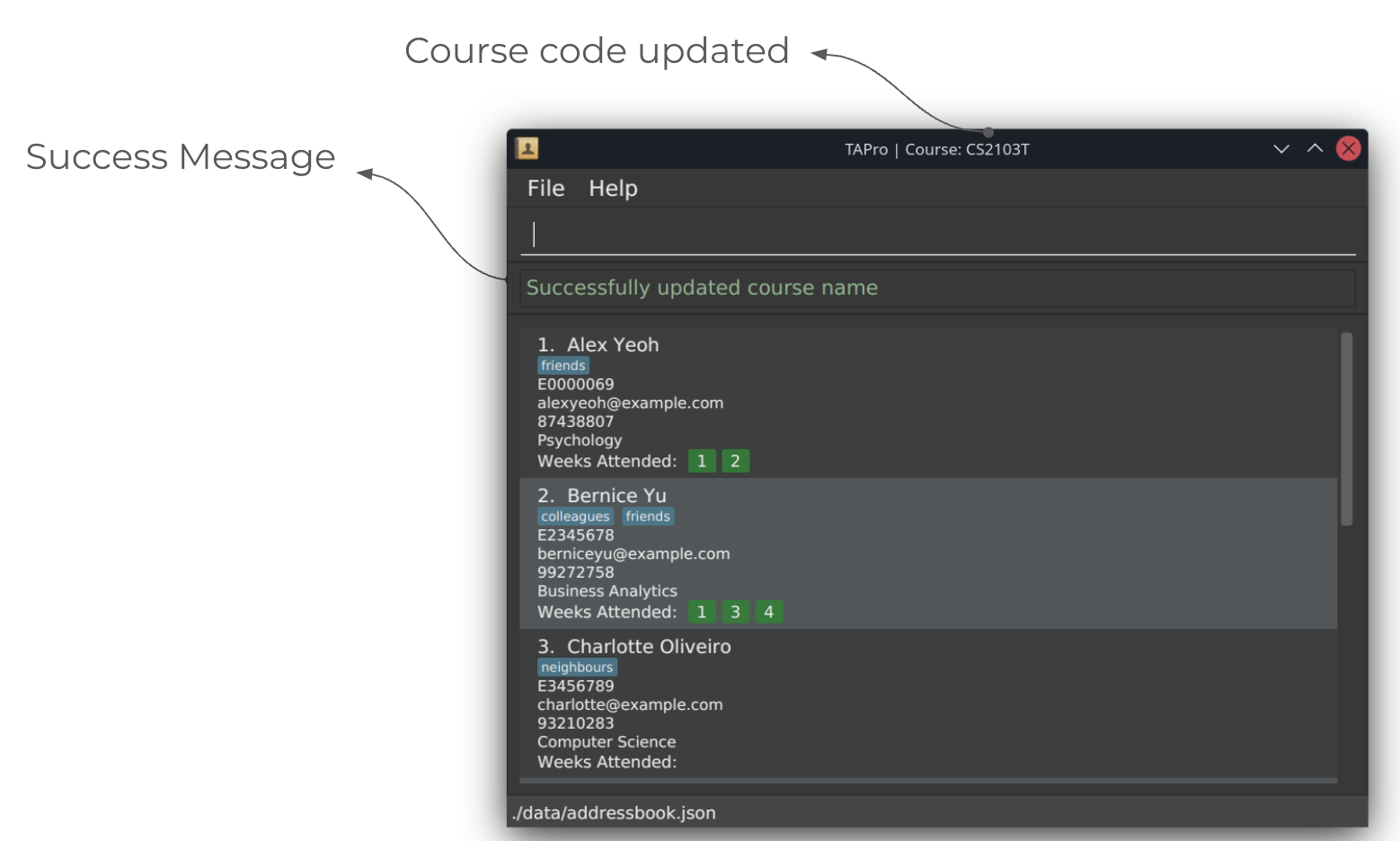
Name/Rename CS course : setcrs
Sets the course code in question.
Format: setcrs COURSE_CODE
The course code is shown at the top of TAPro's main window.
Course code must be in the format
XX1234Y, whereYis optional.
Course codes are case-insensitive.
Course code is meant for CS coded courses, hence only a prefix of two letters is allowed.
Examples:
setcrs cs2103tsetcrs CS2030
Screenshots of using the setcrs command:
Before running setcrs command:
After running setcrs command:
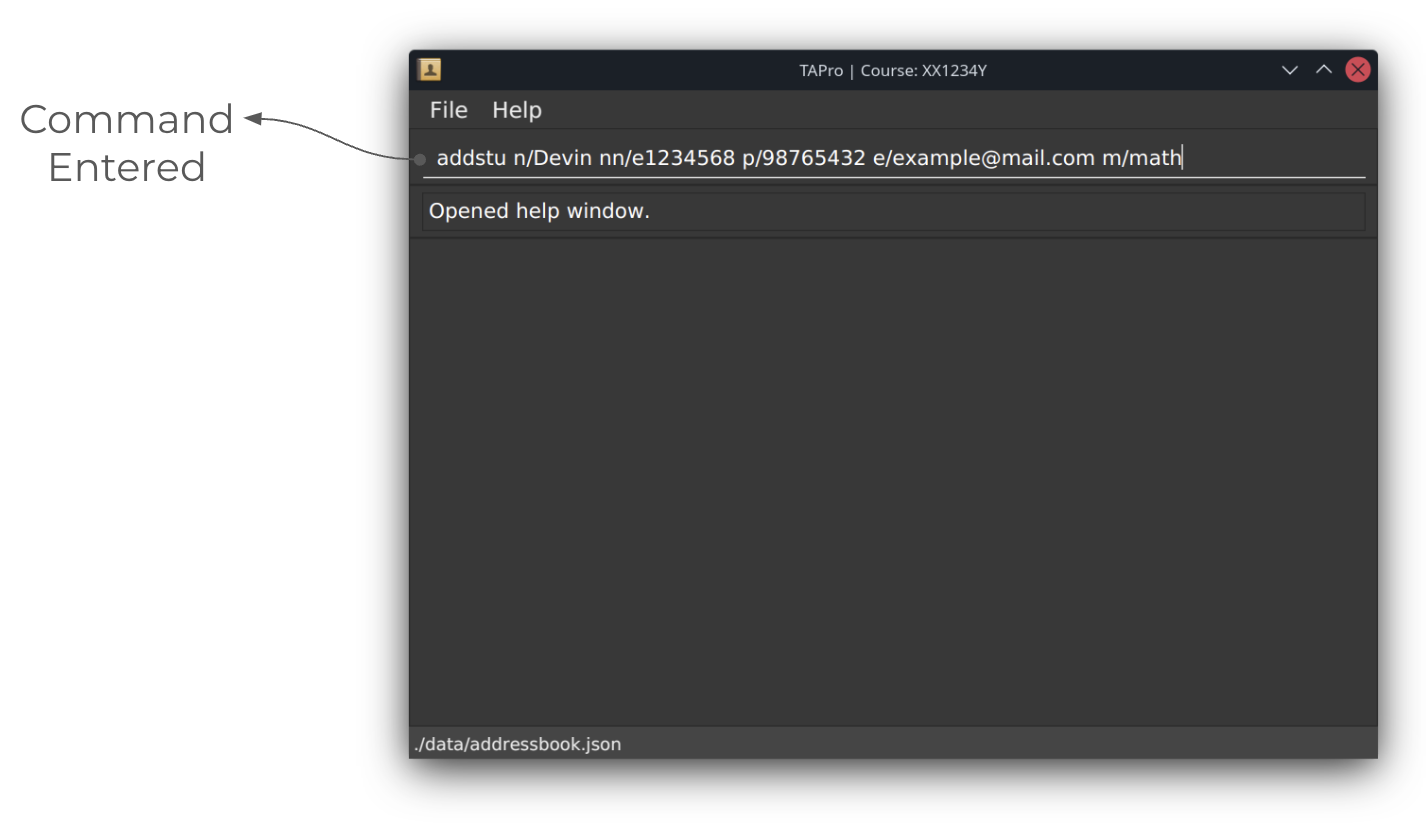
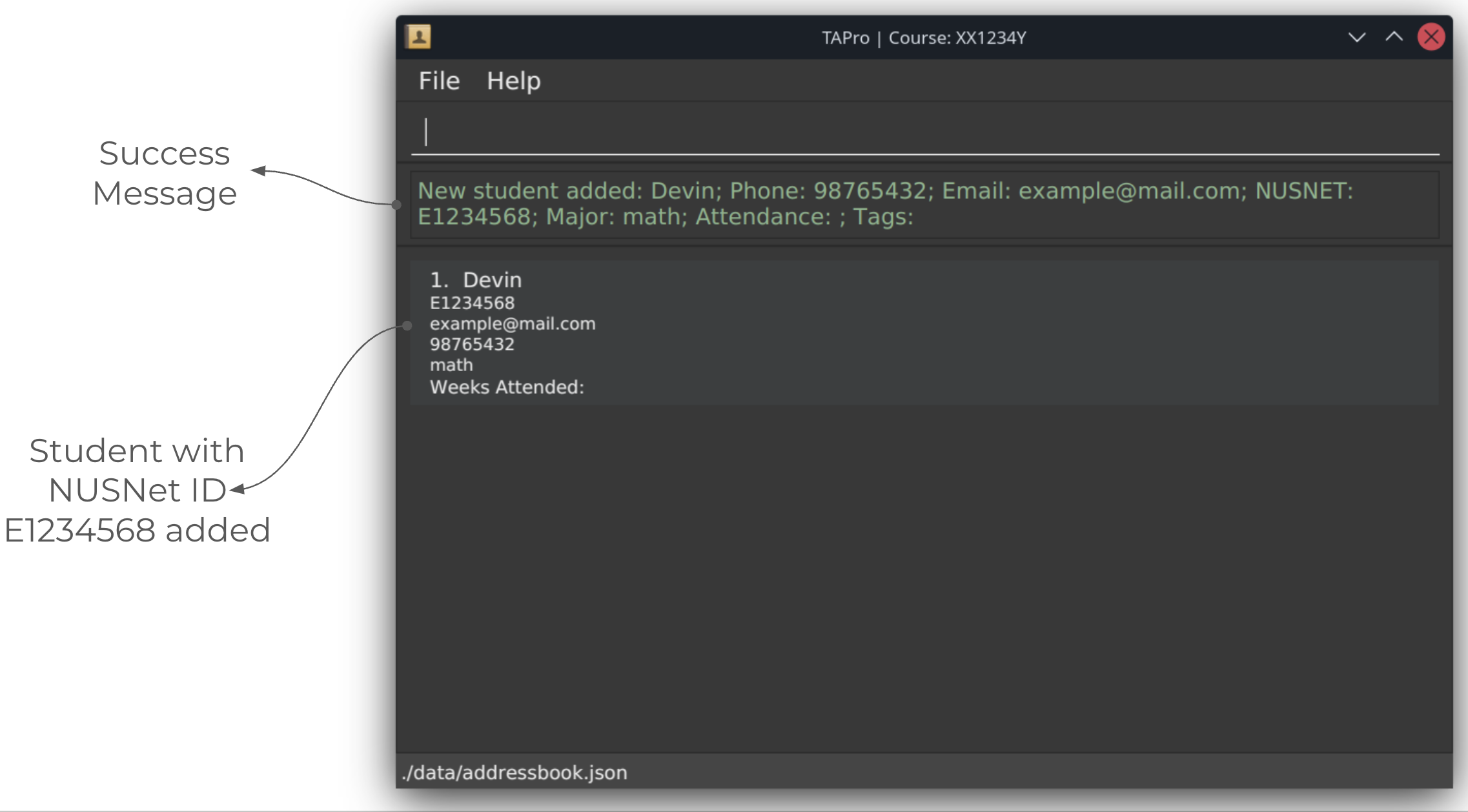
Adding a student: addstu
Adds a student to the contact book.
Format: addstu n/NAME nn/NUSNET [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [m/MAJOR] [t/TAG]…
Adds a student with the given details.
The name and NUSNet ID must be provided, as they are not optional parameters.
And NUSNet ID must be unique.
Case-insensitivity of NUSNet ID:
NUSNet ID is case-insensitive, and it will be converted to uppercase automatically upon running the command.
For example, e0123456 will be converted to E0123456, as E0123456 and e0123456 refer to the same NUSNet ID.
- Name must not be empty (or spaces only), and must have single spaces between words. It must be in proper-case and contain only alphabets.
Adding un-permitted names:
In the current version of TAPro, certain names are not permitted due to the strictness of name validation.
The current workaround is to follow the proper-case format and make slight changes to the name, so that the validation works.
Example: For names like Zubir bin Said and Balaji s/o Sadasivan, we can make slight changes to the name to fit current permitted formats.
They become Zubir Bin Said and Balaji So Sadasivan after the change, which are still similar enough to the original to not cause confusion.
- All the remaining fields are optional. If values are not provided to optional fields, they will be set to a placeholder value under the hood (e.g.,
Major not providedforMAJORfield).
Any number of tags:
A student can have any number of tags, including 0.
Alphanumeric tags
bestFriend4Ever, colleague, Club are valid tags, but best friend, best-friend are not valid tags.
Adding new tag(s) will replace the existing tag(s)
Adding multiple majors:
If a student is undertaking a double degree programme, you can use a comma to separate the disciplines in the MAJOR field.
Example: We can use m/Computer Science, Mathematics to indicate that a student has these two majors, Computer Science and Mathematics.
Examples:
addstu n/John Doe nn/E1234567 p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com m/Computer Scienceaddstu n/Betsy Crowe nn/E0123456 t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com m/Mathematics, Physics p/1234567 t/clubaddstu n/Betsy Crowe nn/E0123456
Screenshots of using the addstu command:
Before running addstu command:
After running addstu command:
Listing all students : list
Shows a list of all persons in the contact book.
Format: list
- Additional arguments after
listwill be simply ignored.
Screenshots of using the list command:
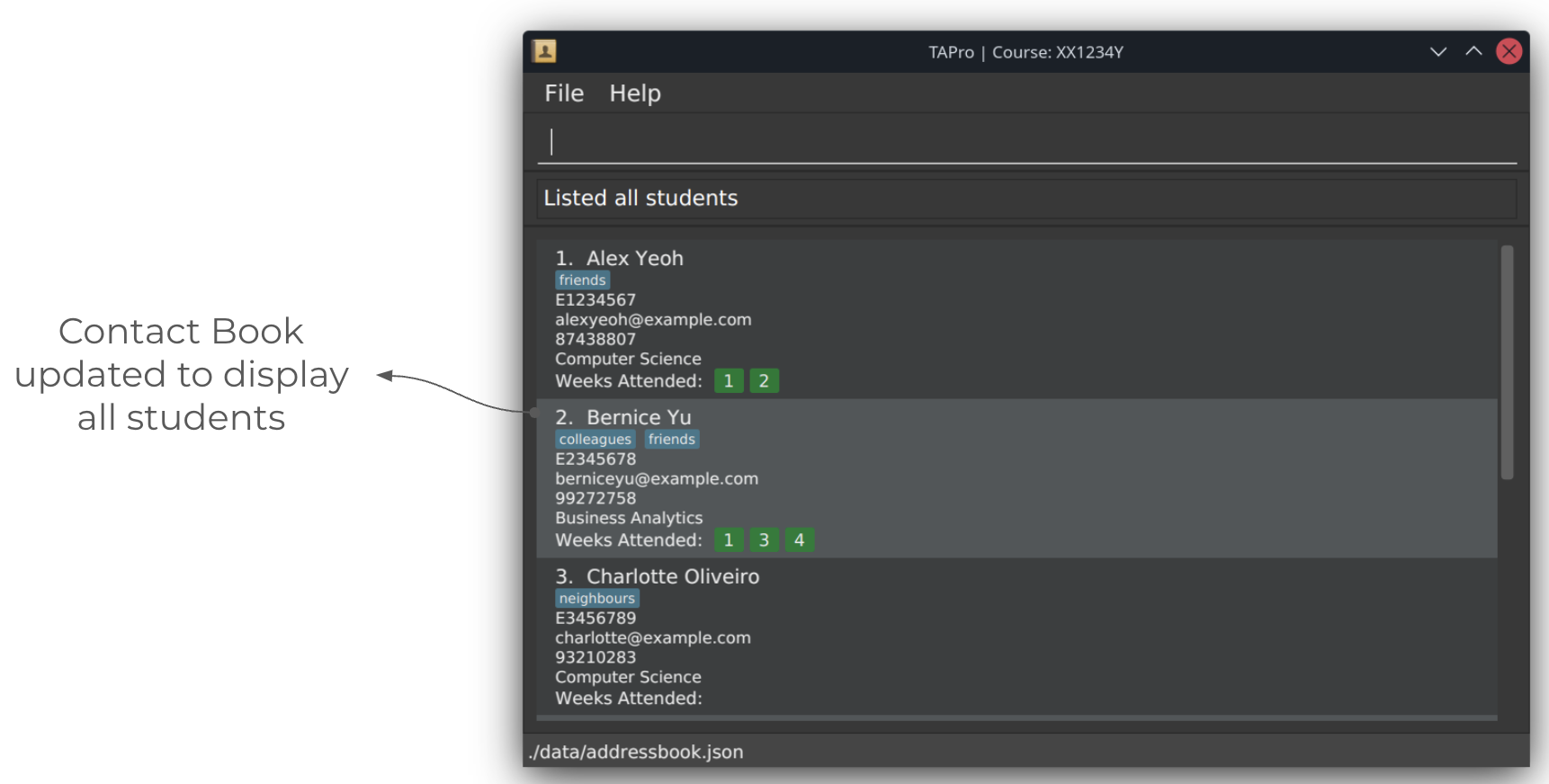
Before running list command:
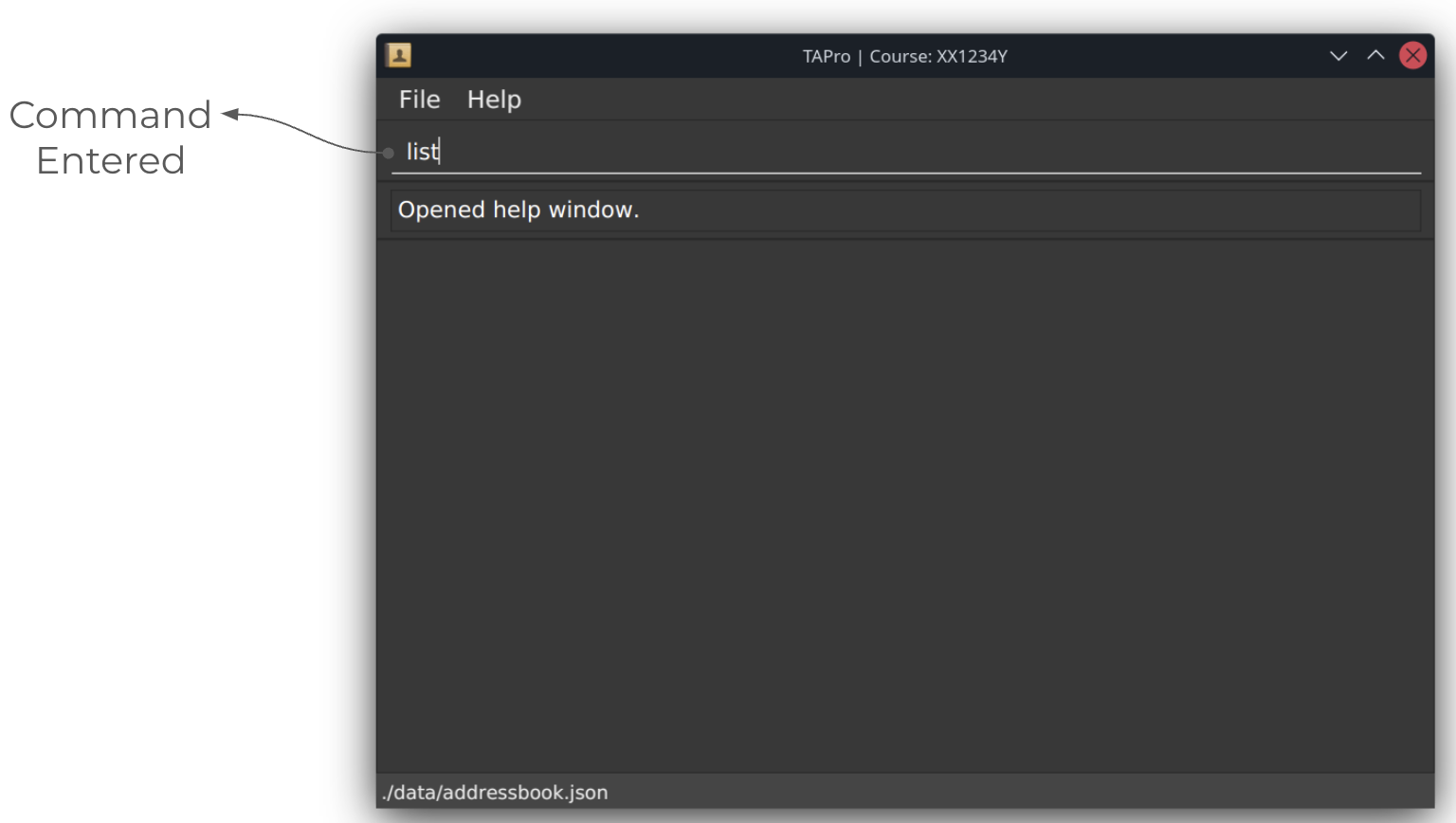
After running list command:
Editing a student : edit
Edits an existing student in the contact book.
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [m/MAJOR] [nn/NUSNET] [t/TAG]…
- Edits the student at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed student list. The index must be a positive integer, such as 1, 2, 3, …
This command differs from most other commands that uses NUSNET to identify a student. This command uses the index number shown in the displayed person list to identify the student to be edited.
At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
Existing values will be updated to the input values.
When editing tags, the existing tags of the student will be removed, i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
You can remove all the student’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it.
When t/ is specified in the command, no other tags can be present, in order to remove all of a student's tag.
Otherwise, TAPro will parse the input as adding multiple tags, which may lead to an unsuccessful execution of the command.
Example: Entering edit 1 t/abc t/ will cause the error message Tags names should be alphanumeric to be shown. This error message is shown because TAPro expects the second t/ to contain an alphanumeric value, which an empty value is not.
Examples:
edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email contact of the first student to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively.edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/Edits the name of the second student to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
Screenshots of using the edit command:
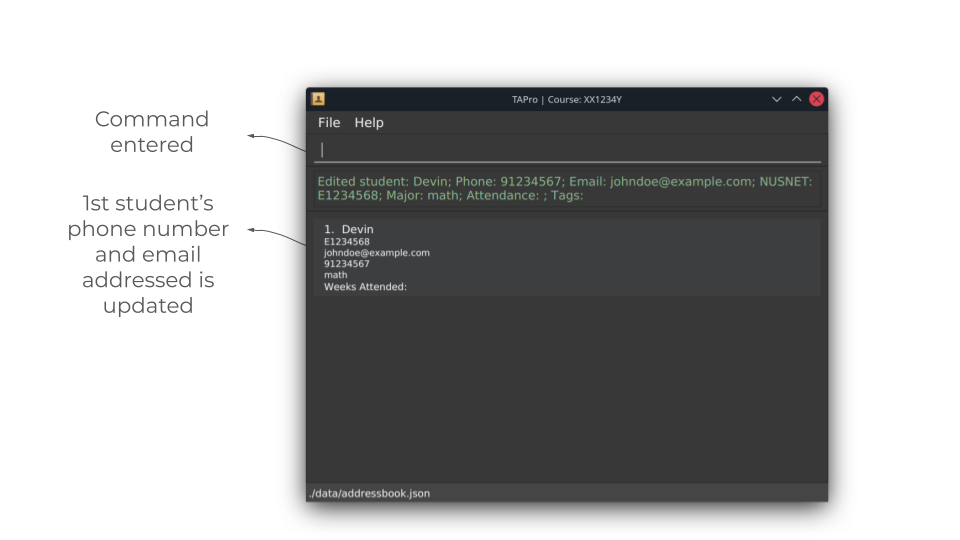
Before running edit command:
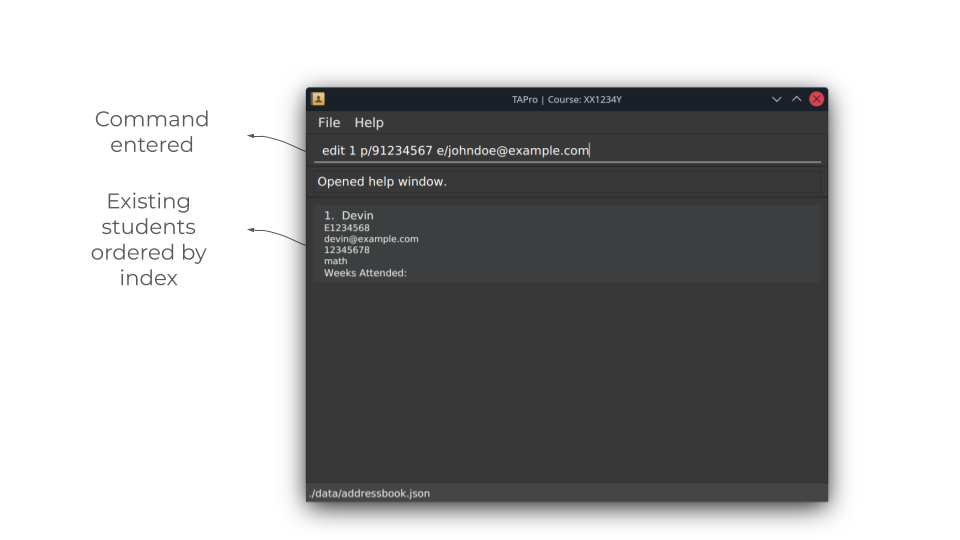
After running edit command:
Locating students by name: find
Finds students whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]…
Parameters of find command:
Both KEYWORD and [MORE_KEYWORDS]… accept alphanumeric and special symbols as their supplied value, and are separated by spaces when supplied.
KEYWORDis the first keyword to search for. This is a compulsory parameter.[MORE_KEYWORDS]…are additional, optional keywords to search for. You can have any number of additional keywords.
About the find command:
Only the name is searched.
Example: E01234567 will not match a student with NUSNet ID E01234567.
The name search is case-insensitive.
Example: hans will match Hans
The order of the keywords does not matter.
Example: Hans Bo will match Bo Hans
Only full words will be matched.
Example: Han will not match Hans
Students' name matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e. OR search).
Example: Hans Bo will return Hans Gruber, Bo Yang
Find does not give any error message when invalid parameters are supplied.
Examples of using the find command:
Example: find John returns john and John Doe
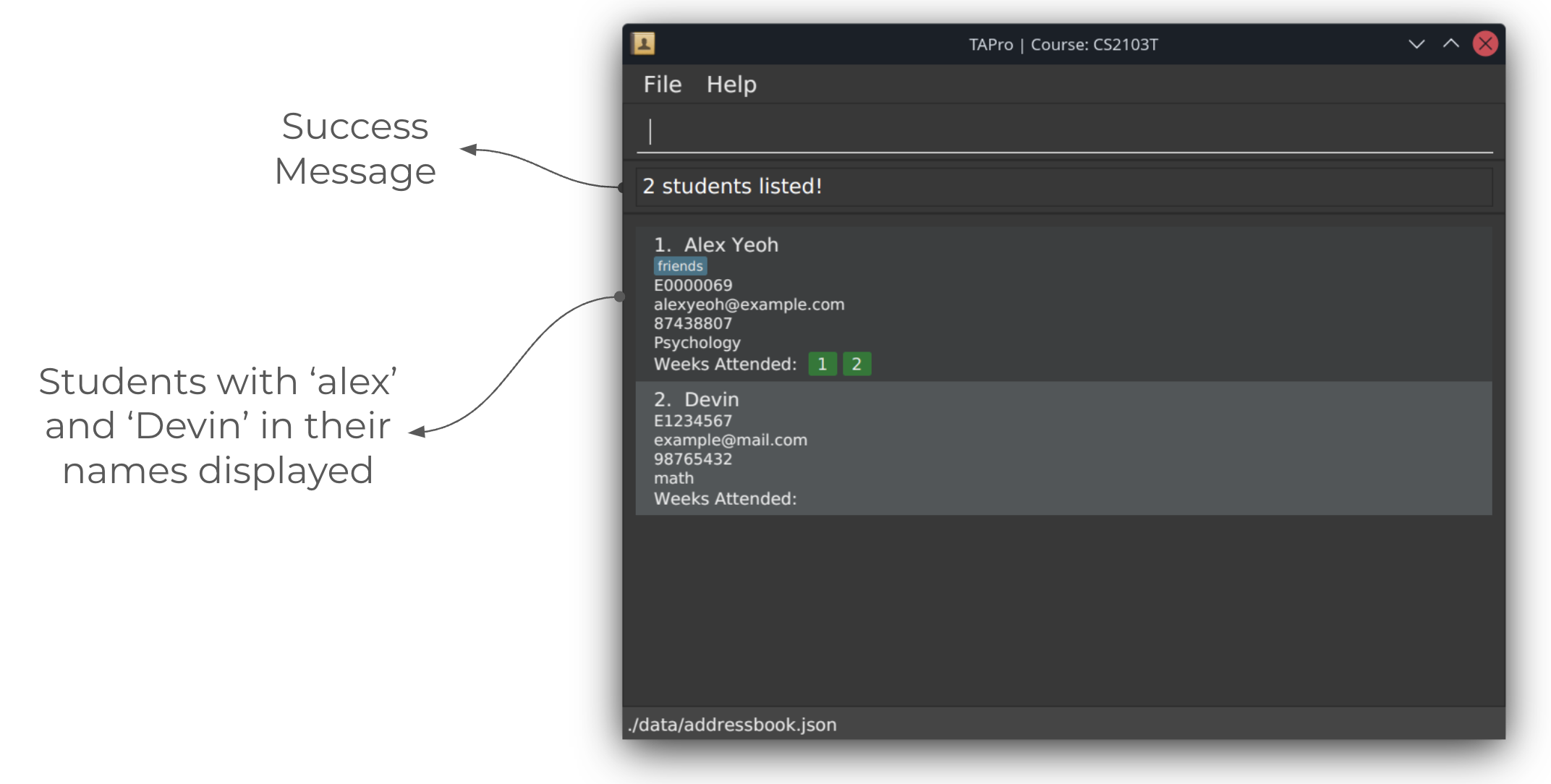
Example: find alex david returns Alex Yeoh, David Li, as seen in the image below.
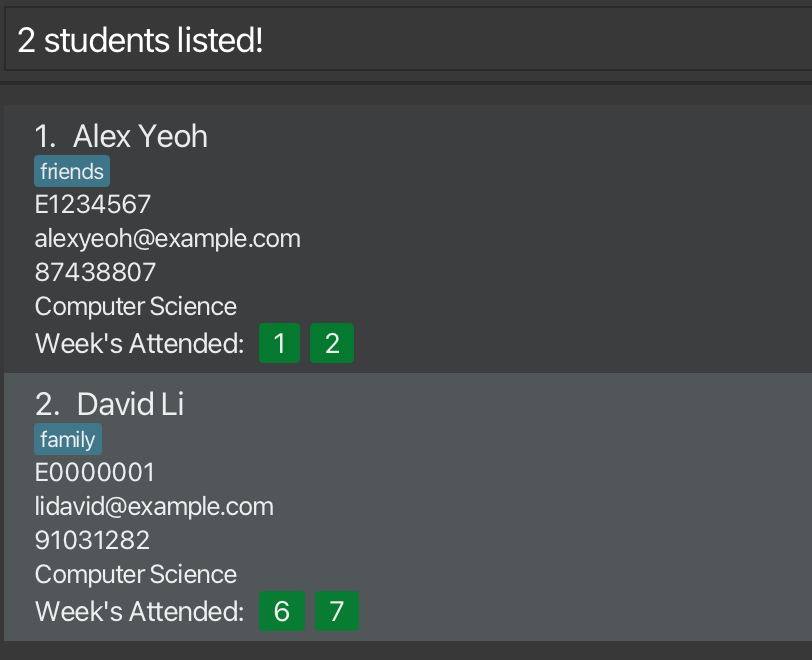
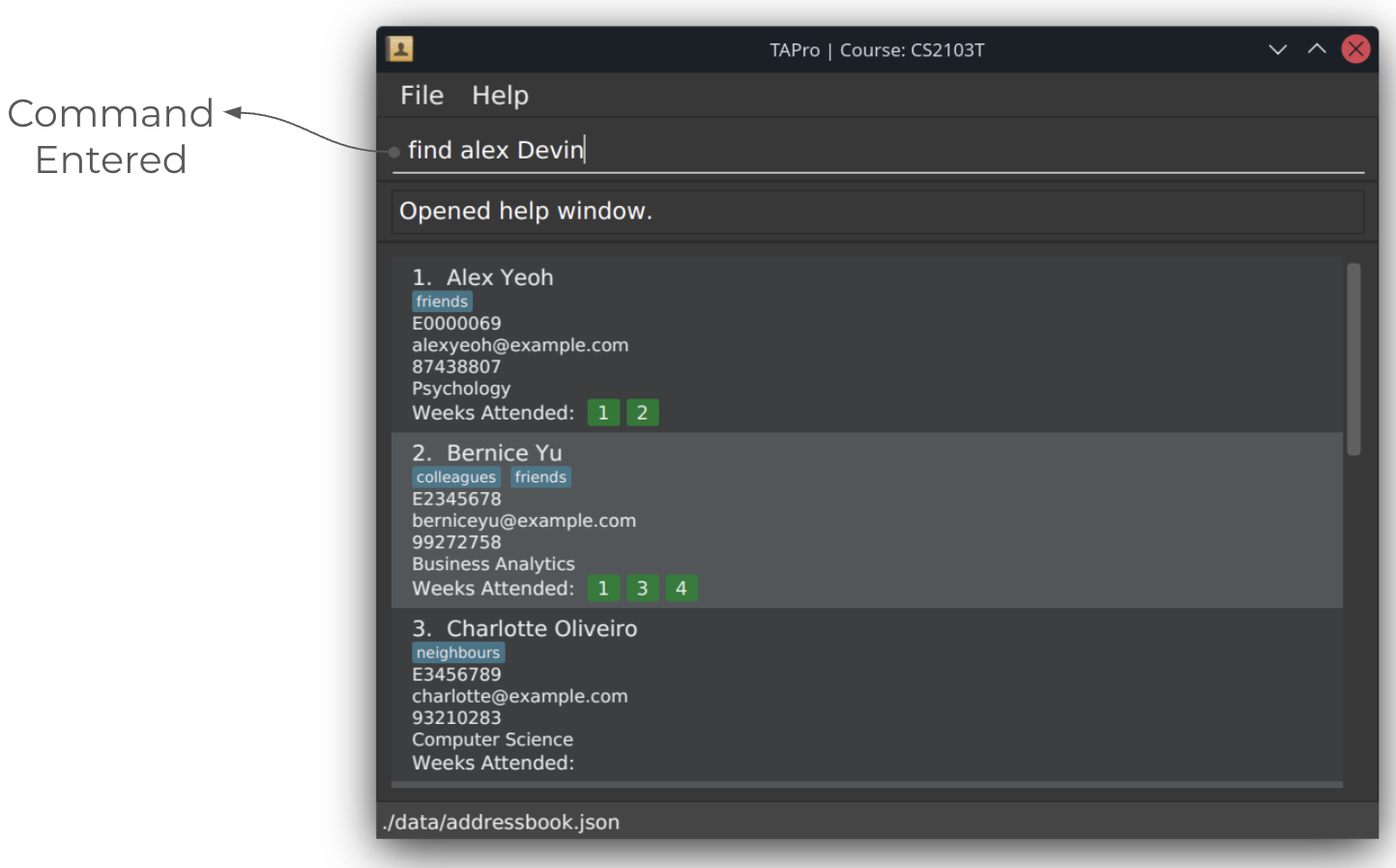
Screenshots of using the find command:
Before running find command:
After running find command:
Marking a student's attendance for a given week by their NUSNet ID: mark
Marks a student's attendance for a particular week.
Format: mark nn/NUSNET wk/WEEK
Example: mark nn/E1234567 wk/3
Screenshots of using the mark command:
Before running mark command:
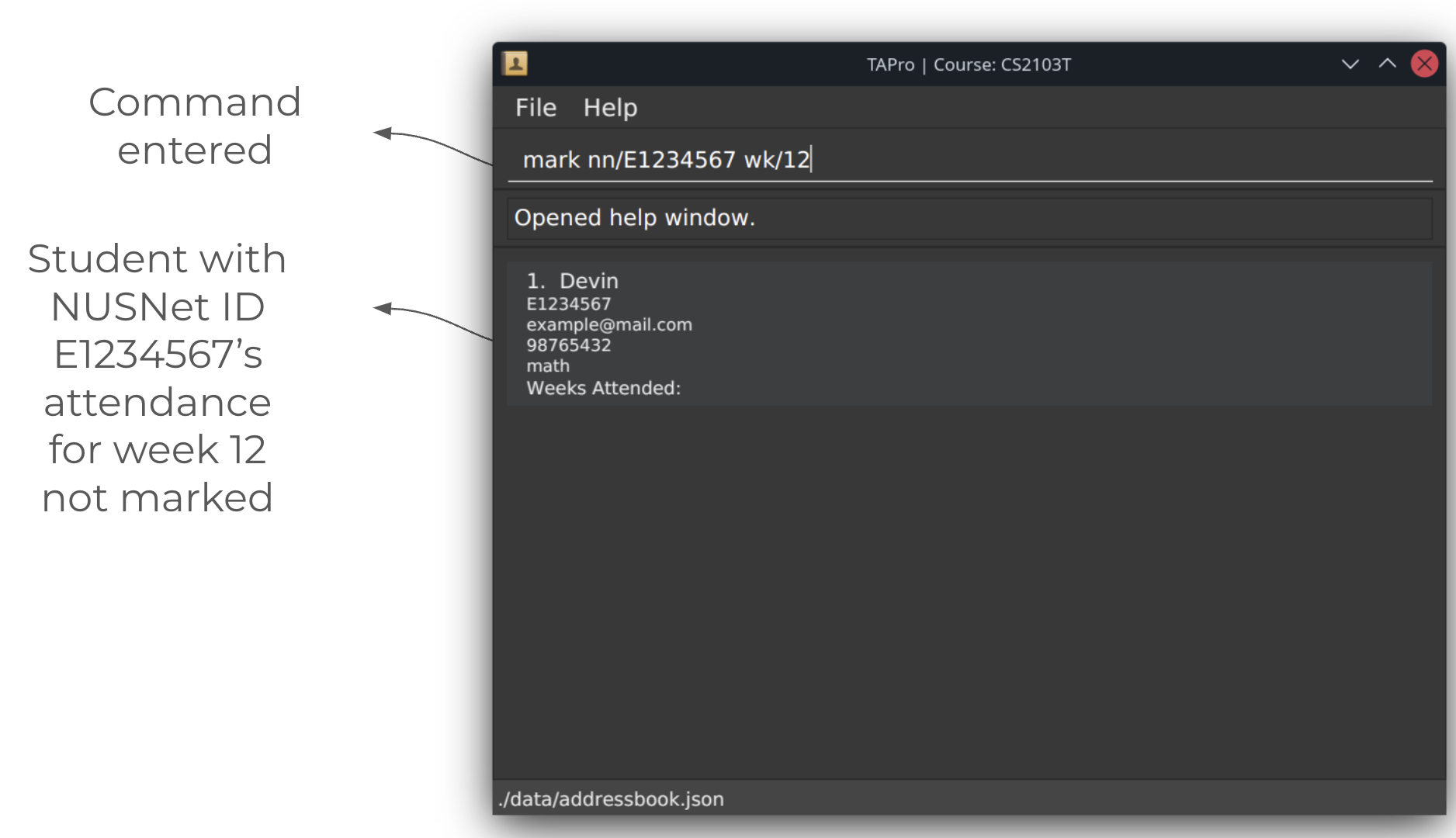
After running mark command:
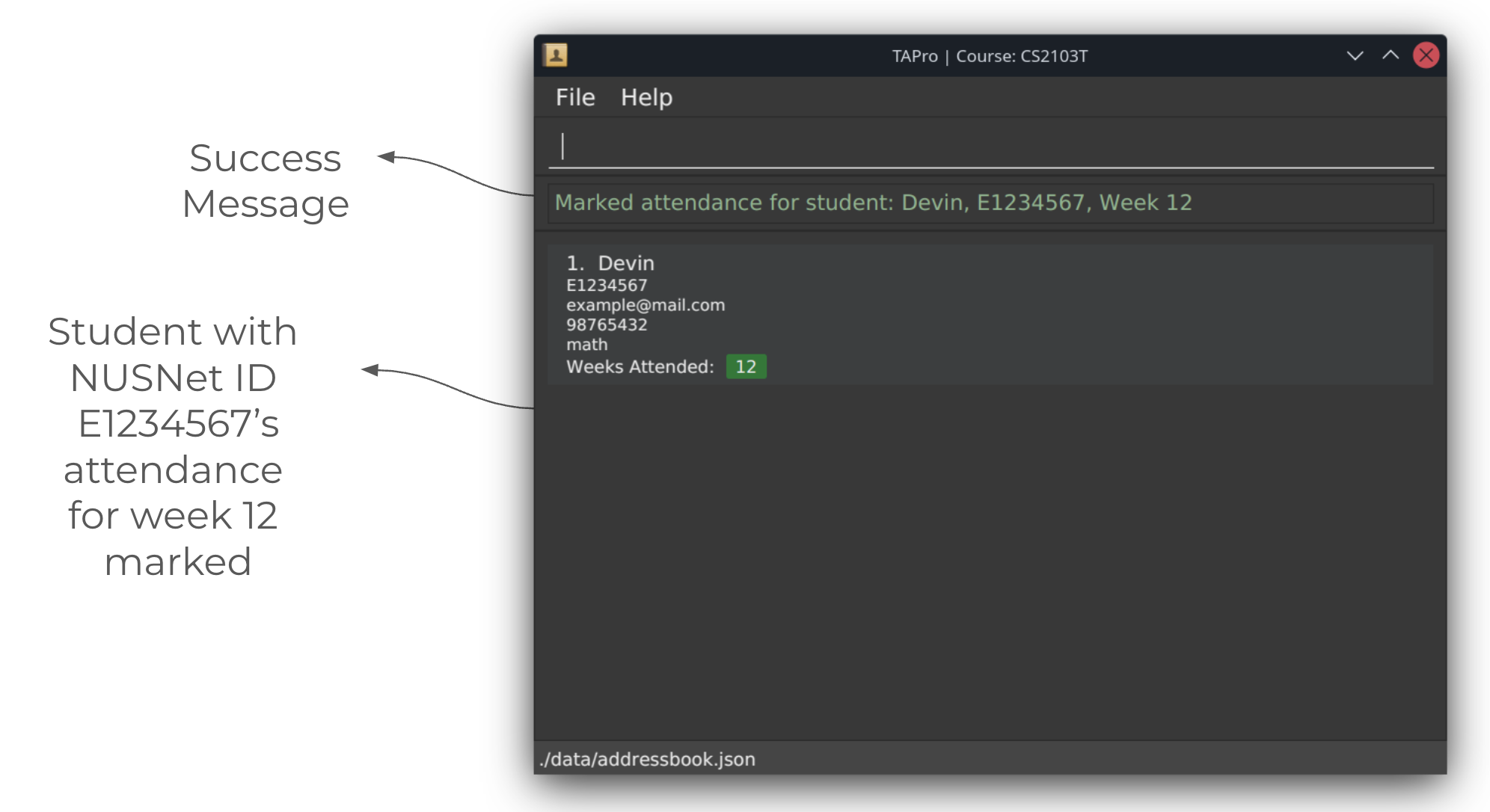
Unmarking a student's attendance for a given week by their NUSNet ID: unmark
Unmarks a student's attendance for a particular week.
Format: unmark nn/NUSNET wk/WEEK
Example: unmark nn/E1234567 wk/3
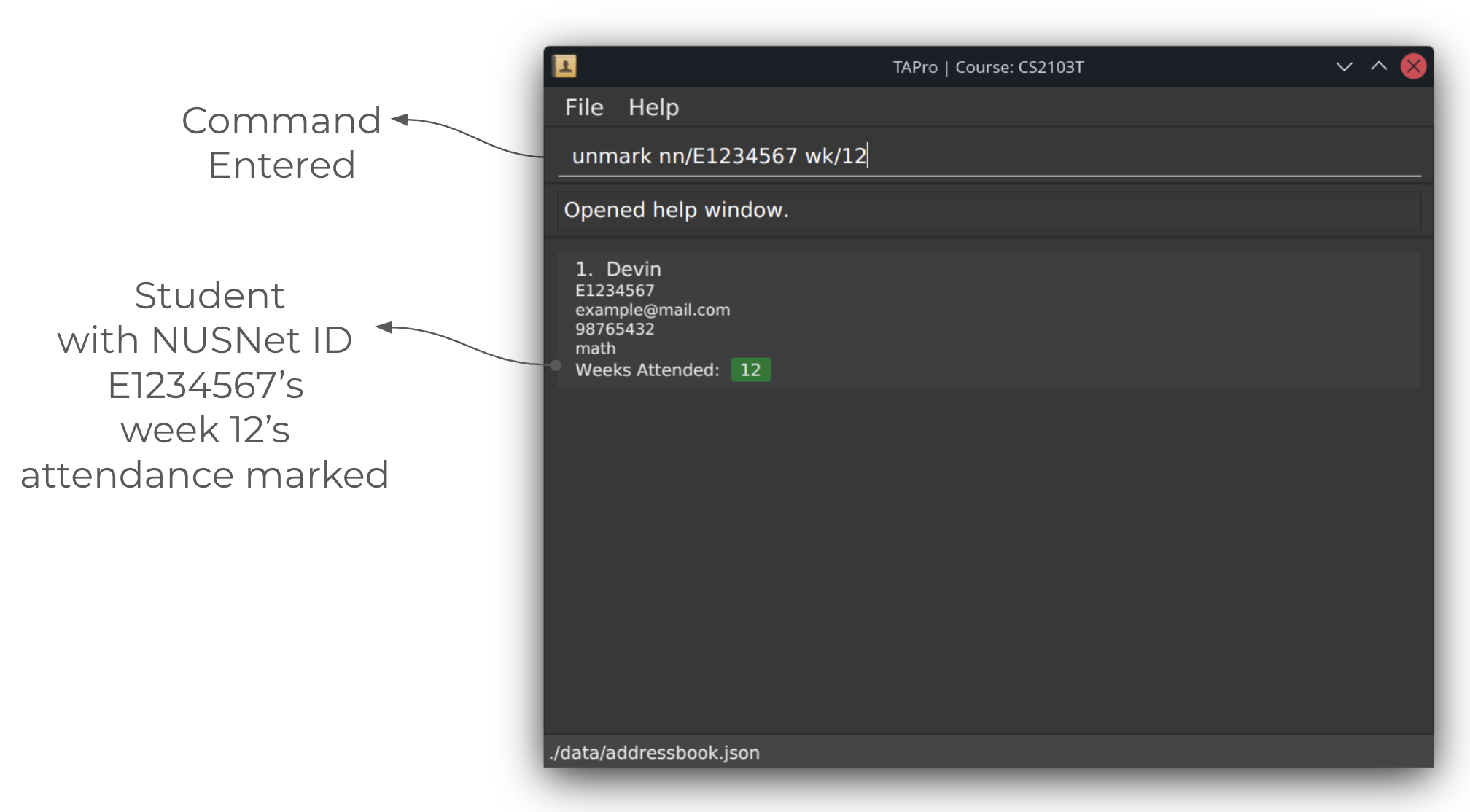
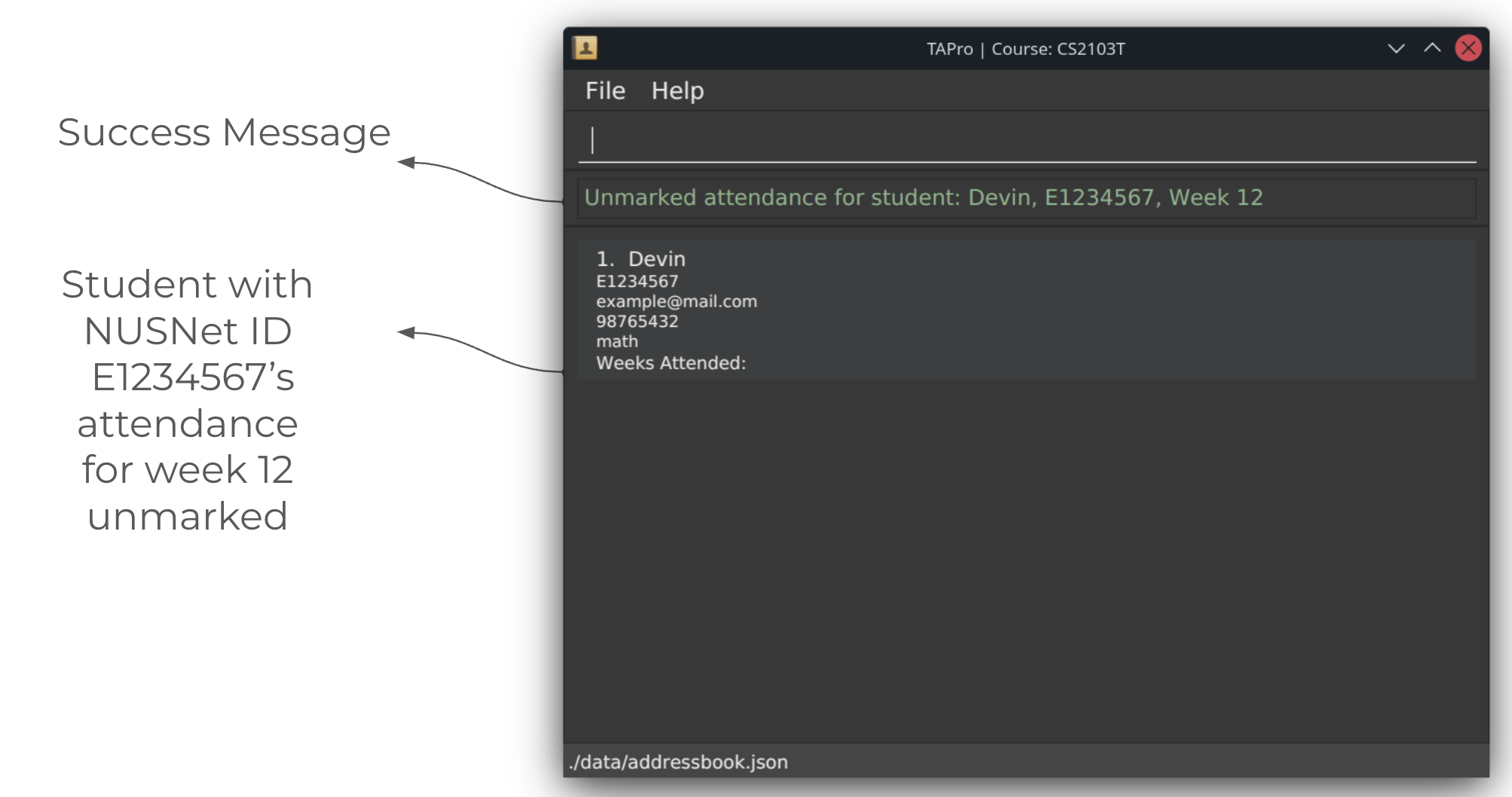
Screenshots of using the unmark command:
Before running unmark command:
After running unmark command:
Deleting a student: delstu
Deletes the specified student from the contact book.
Format: delstu nn/NUSNET
- Deletes the student with the specified NUSNet ID from the contact book.
Example: delstu nn/E0957499 deletes the student with the NUSNet ID of E0957499 from the contact book.
Easily find and delete students:
If you cannot remember your student's NUSNet ID, you could use find Betsy or list followed by delstu nn/<Betsy's NUSNET> to find and delete the student.
Screenshots of using the delstu command:
Before running delstu command:
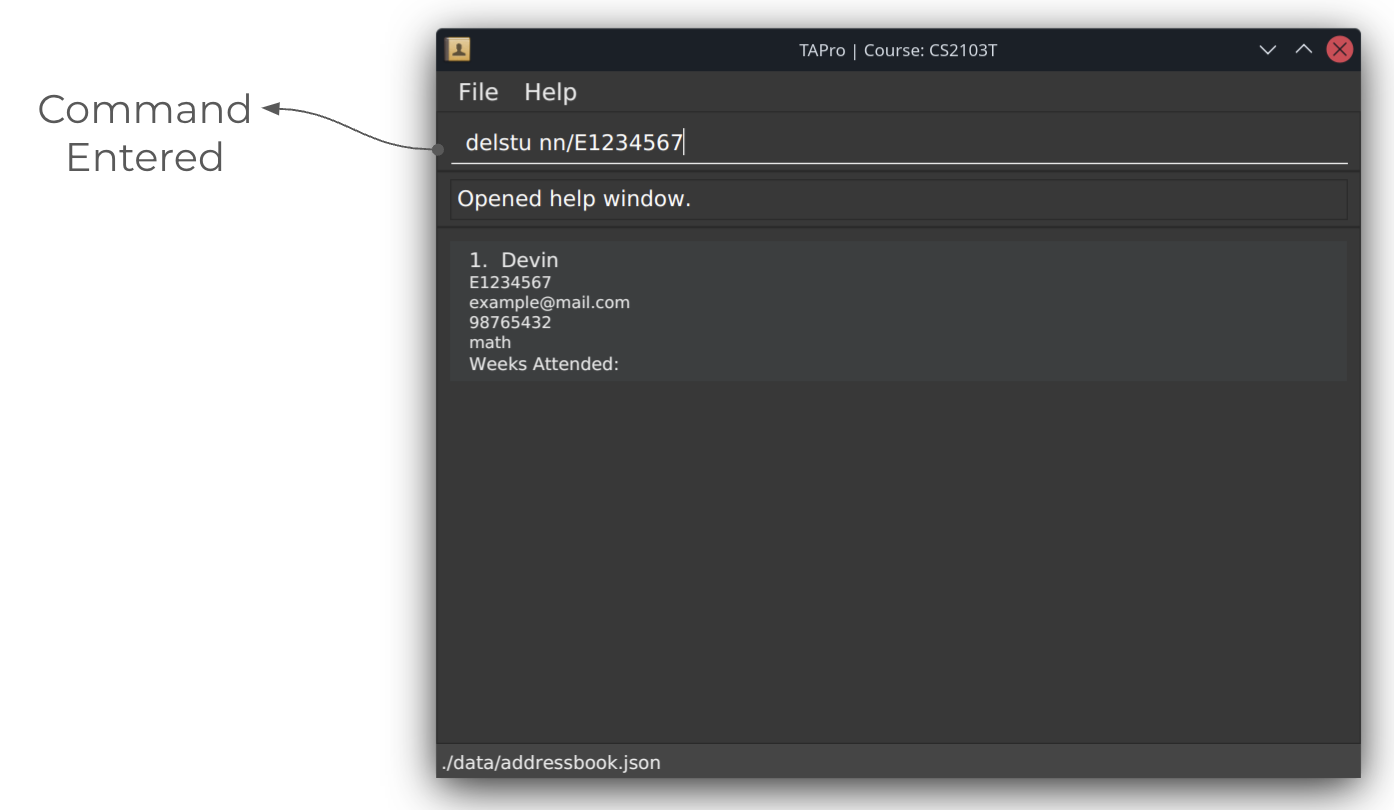
After running delstu command:
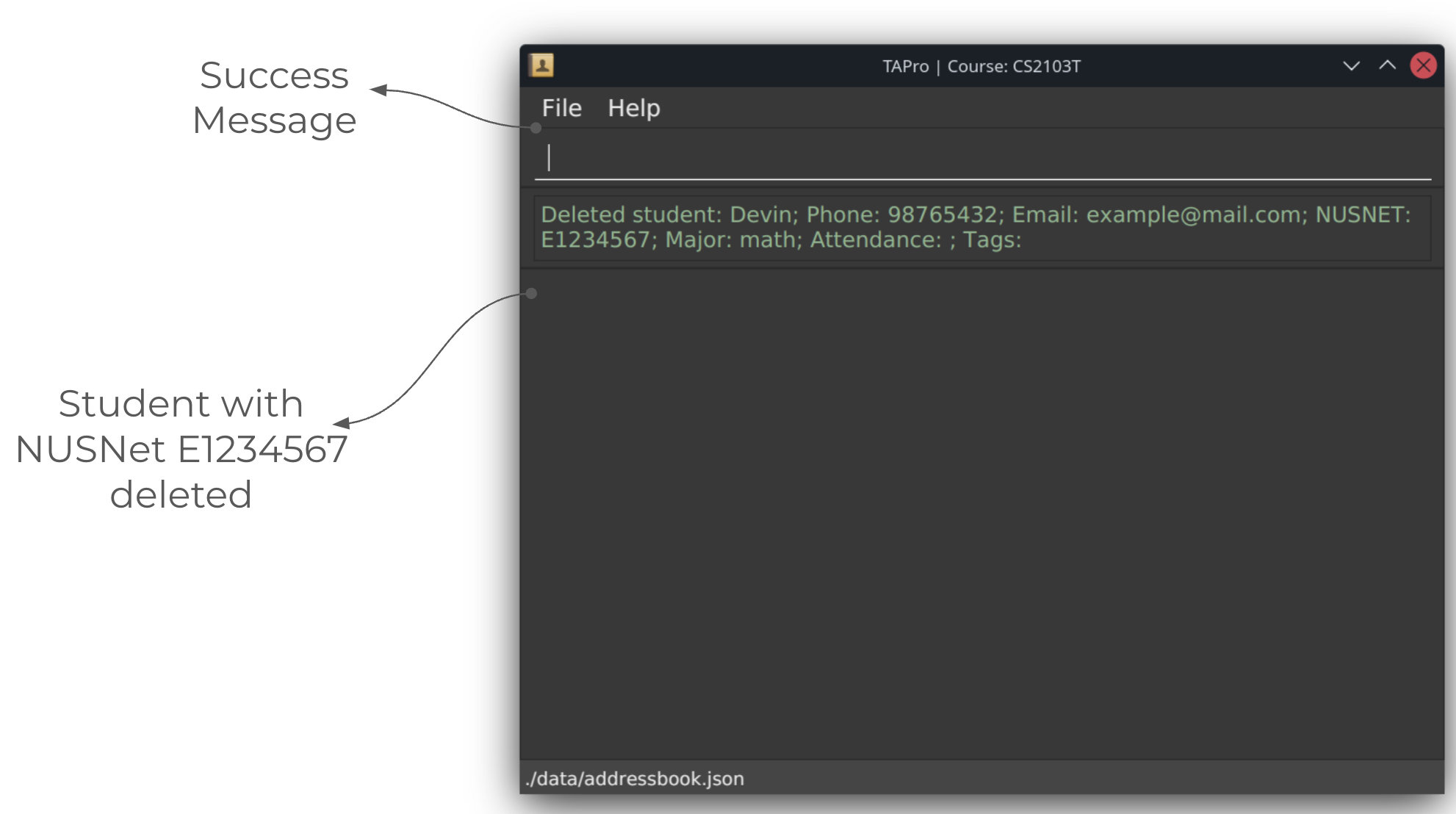
Clearing all entries : clear
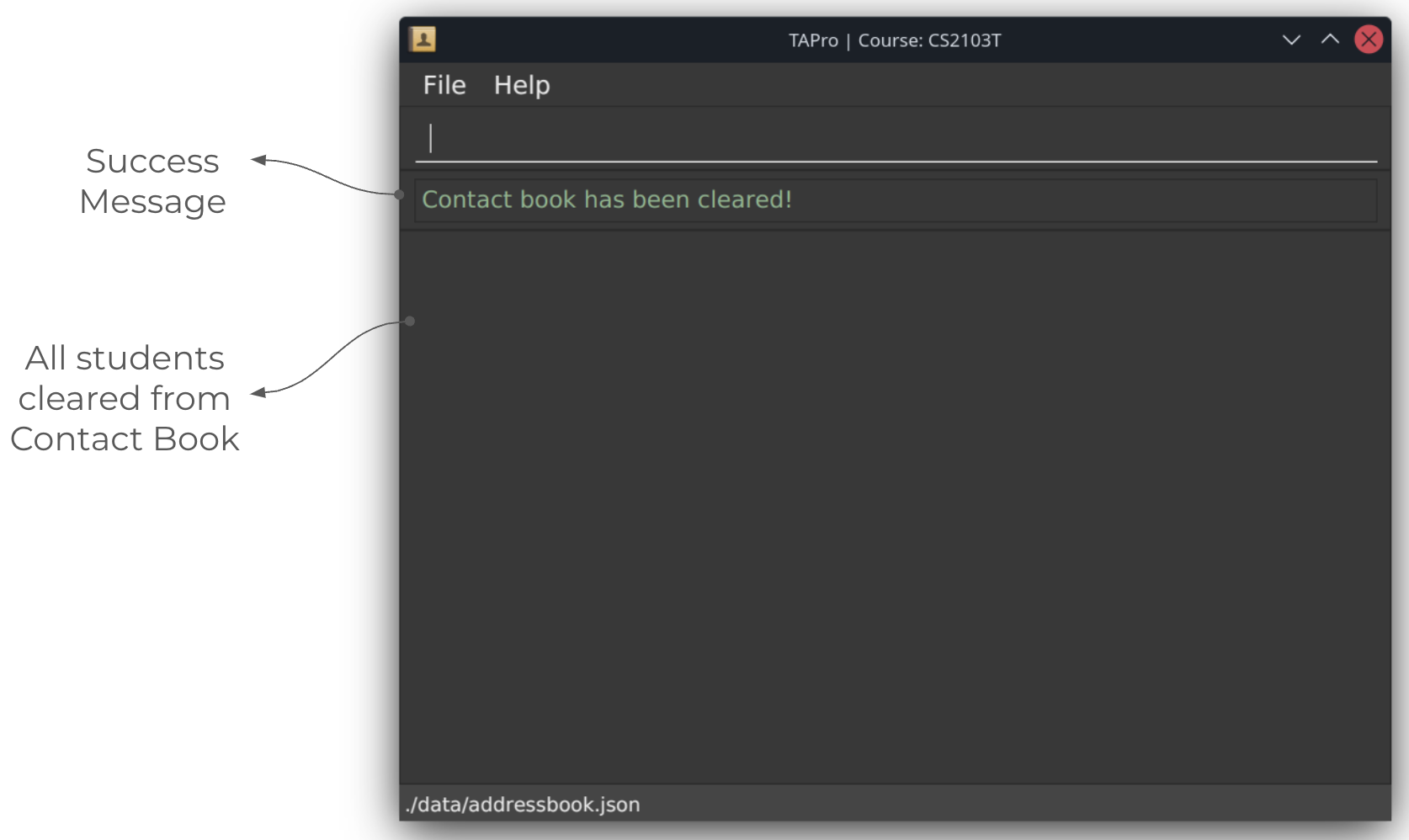
Clears all entries from the contact book.
Format: clear
- Additional arguments after
clearwill be simply ignored.
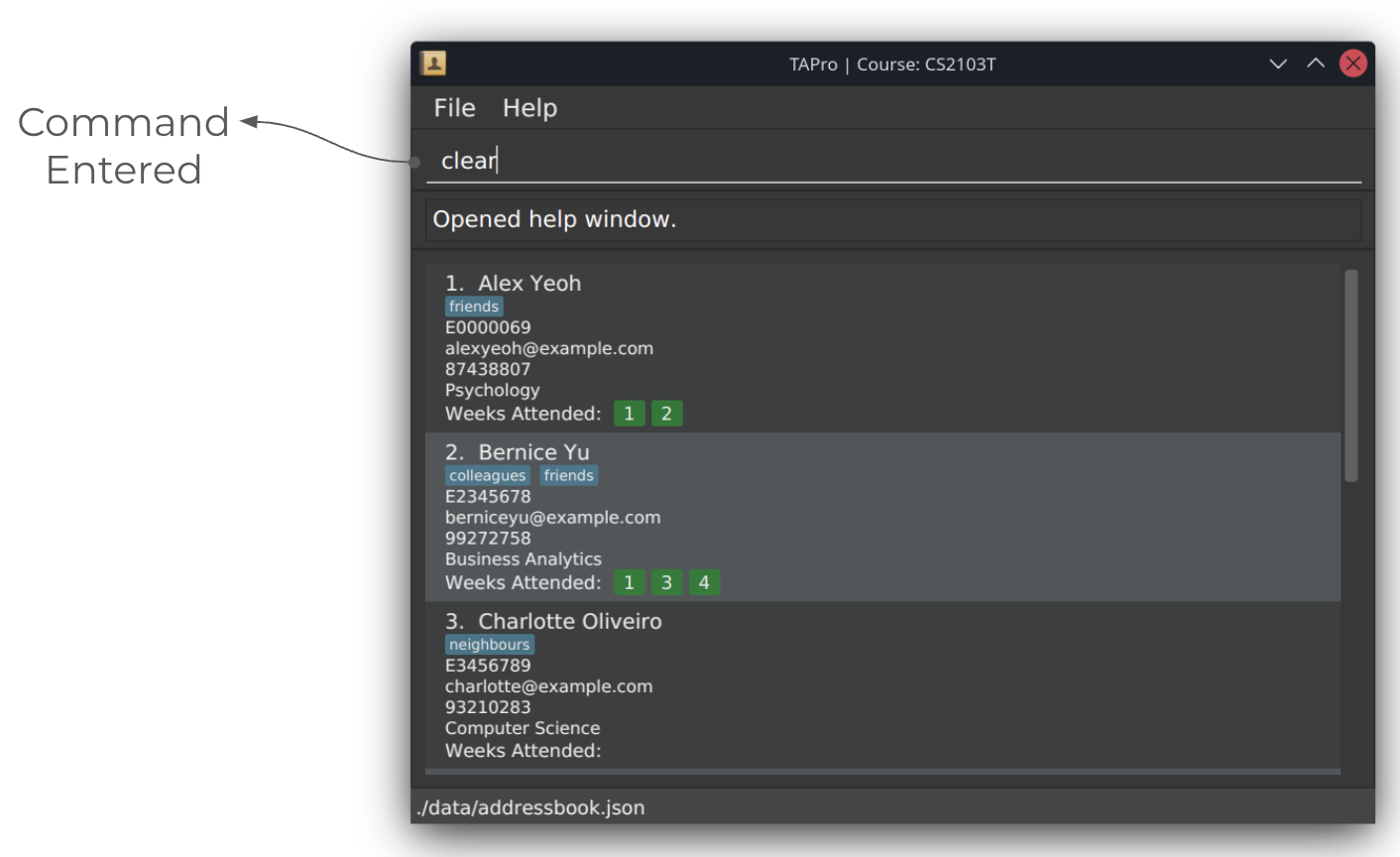
Screenshots of using the clear command:
Before running clear command:
After running clear command:
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
- Additional arguments after
exitwill be simply ignored.
Screenshots of using the exit command:
Before running exit command:
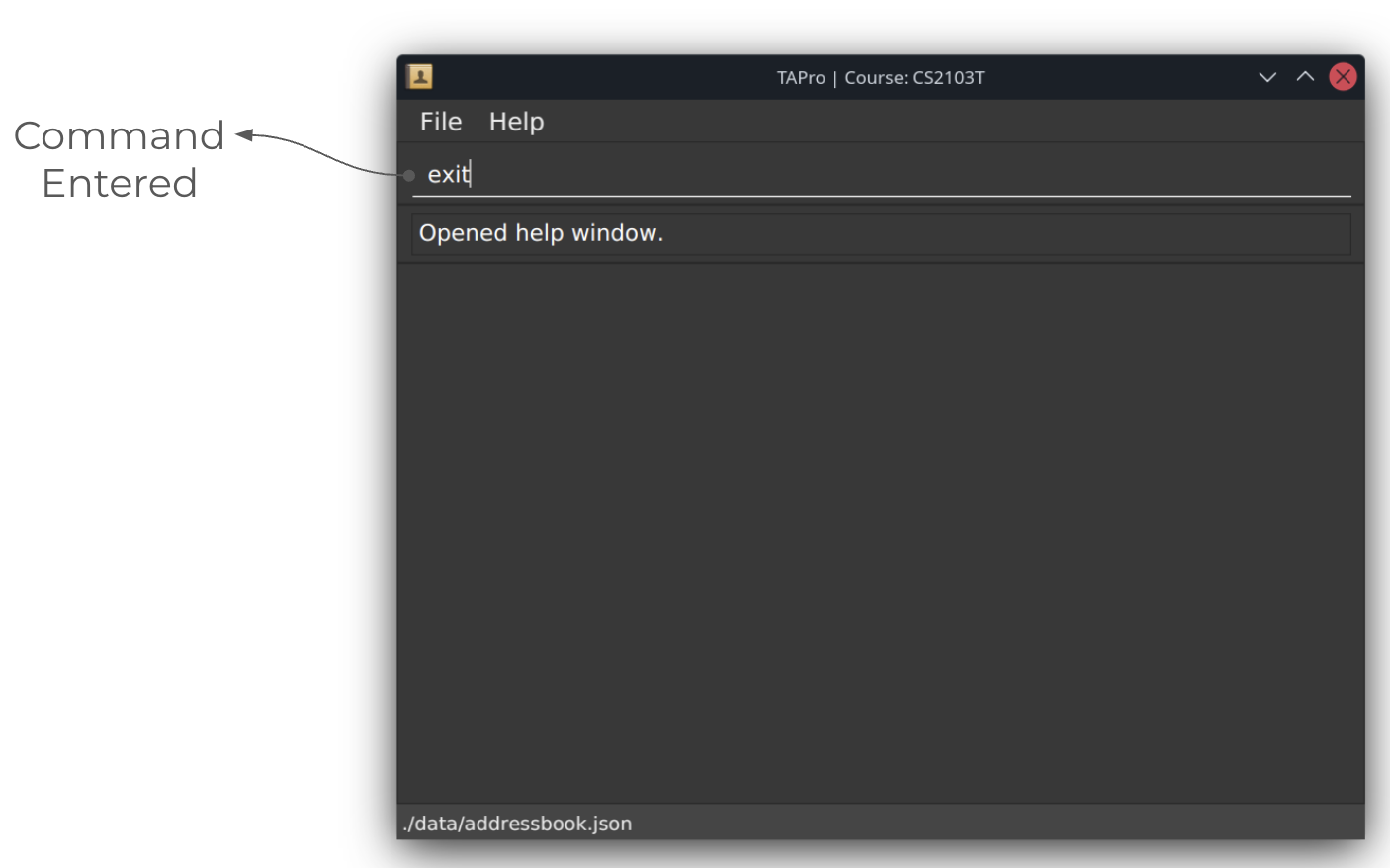
Autocomplete
The autocomplete feature autocompletes a parameter or command, based on the current command box input and the current data in TAPro. This means that if an attribute value is not present, it will not be present in the autocompletion of that corresponding parameter.
Autocompletion: The autocomplete feature's suggested result(s).
- We can autocomplete both command names and parameters after their prefixes by pressing TAB, when an autocompletion is available.
Autocompletes the first word as a command name:
The first word, will be autocompleted as a command name, instead of a parameter, if an autocompletion can be found for the current word that is in the command box input.
Example:
We have three students with NUSNet IDs E0123456, E1234567 and E2345678.
If we type mark nn/ into the command input box and press TAB ,
we can see that the text in the command input box autocompletes to become mark nn/E01234567.
Pressing TAB again, causes the text to update to mark nn/E1234567,
followed by mark nn/E2345678.
If we type a into the command input box and press TAB, we see that the text in the command input box autocompletes to become addstu.
The last parameter TAG is autocompleted.
Autocompletes the last parameter in the input:
Autocomplete works on the last parameter (if any) in the command box, which is the text directly after a recognized prefix.
A parameter can only be autocompleted if it is not the first word, and has a recognized prefix.
Example:
We have some students in TAPro, such that the first tag alphabetically is friends.
If we type edit 1 n/John Doe t/ into the command input box and press TAB,
we see that the text in the command input box autocompletes to become edit 1 n/John Doe t/friends.
The last parameter TAG is autocompleted.
Autocomplete scrolls through all autocompletions:
Autocomplete will scroll through all possible suggestions, based on the existing data in your contact list.
When reaching the end of the all possible suggestions, pressing TAB will wrap the possible options back to the start of that list again.
Example:
We have three students with NUSNet IDs E0123456, E1234567 and E2345678.
If we type mark nn/ into the command input box and press TAB,
we can see that the text in the command input box autocompletes to become mark nn/E0123456.
Every press of TAB, causes the command input box text to update to the next autocompletion:
- from
mark nn/E0123456tomark nn/E1234567, - then to
mark nn/E2345678, - and then back to
mark nn/E0123456.
Autocomplete is omitted on week number.
Autocomplete does not work for week number, because WEEK is at most two digits, so it is much faster just typing out the number.
Sorted autocompletions:
The autocompletions will be listed in ASCIIbetical order, which is when all uppercase letters come before lowercase letter, and digits and most punctuations come before letters.
Example:
If we have only the following tags in our contact list: abc, 123 BCD, 234, bcd, autocompleting a TAG will give autocompletions in this order: 123, 234 BCD, abc, bcd.
Quickly clear an attribute with autocomplete:
We can autocomplete the placeholder value, if it is present for that parameter in our contact list. When a placeholder value is inputted as the parameter, it means that attribute for that student will be reset, after entering the command.
Example:
If the placeholder for the MAJOR parameter, Major not provided, is present in the contact list, then in the autocompletion for the MAJOR parameter, the value Major not provided is available.
Retrieving command history
TAPro saves successful commands input, so you can retrieve them later, using the UP and DOWN arrow keys.
Example:
mark nn/E0123456was the previous successful command.- Now the command input box is empty.
- Pressing UP will
fill the text in the command input box to
the previous command
mark nn/E0123456! - You can press UP continuously to scroll through all the previous commands you have entered.
- Pressing DOWN will scroll back to the more recent commands you have entered.
Current input is erased:
When retrieving commands, be aware that it will erase the current text in the command input box.
Your current input is the latest:
Pressing DOWN without having ever pressed UP will attempt to retrieve a later command, which is empty text, because you are at your most recent command.
Retrieves only successful input:
Only commands that has succeeded previously will be retrieved. If you enter an invalid command, it will not appear when attempting to retrieve it.
Saving the data
TAPro's data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
TAPro's data are saved automatically as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/addressbook.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Invalid data file format:
If your changes to the data file makes its format invalid, TAPro will discard all data and start with an empty data file at the next run. Hence, it is recommended to take a backup of the file before editing it.
Furthermore, certain edits can cause the TAPro to behave in unexpected ways (e.g., if a value entered is outside the acceptable range). Therefore, edit the data file only if you are confident that you can update it correctly.
Command summary
| Action | Format | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Add Student | addstu n/NAME nn/NUSNET [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [m/MAJOR] [t/TAG]… | addstu n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com nn/E1234567 m/Computer Science t/friend t/colleague |
| Clear | clear | clear |
| Delete Student | delstu nn/NUSNET | delstu nn/E0957499 |
| Edit | edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [m/MAJOR] [t/TAG]… | edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com |
| Find | find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]… | find James Jake |
| List | list | list |
| Mark | mark nn/NUSNET wk/WEEK | mark nn/E1234567 wk/3 |
| Unmark | unmark nn/NUSNET wk/WEEK | unmark nn/E1234567 wk/3 |
| Set Course | setcrs COURSE_CODE | setcrs CS2103 |
| Exit | exit | exit |
| Help | help | help |
Known issues
1. Using multiple screens
If you move the application to a secondary screen, and later switch to using only the primary screen, the GUI will open off-screen. The remedy is to delete the preferences.json file created by the application before running the application again.
2. Having more than one instance of TAPro running
If you have more than one instance of TAPro running, the application may not function as expected. TAPro's data will desynchronise. The remedy is to close all instances of TAPro and run only one instance of TAPro.
3. When the data file is in an invalid format
If you edit the data file into an invalid format, upon the next launch of TAPro, no error message would be shown, and all data will be discarded. The remedy is to store a backup of your data file before modifying it, to prevent the loss of data.
FAQ
Transfering Data to Another Computer
Q: How do I transfer my data to another computer?
A: Install the application in the target computer and replace the data folder with the data folder in
your current computer! Click Yes if are prompted to replace the existing data folder in your target computer.
Loading Data from Another Computer
Q: How can I transfer my TAPro contacts to another computer?
A: Install TAPro in your target computer and paste the empty data folder it creates
with the data folder from your otehr computer. Paste it in the same directory as your TAPro JAR file in your
target computer.
Launching TAPro
Q: How can I launch TAPro if clicking on the JAR file does not work?
A: There are two possible methods to launch TAPro.
Method 1: Using the Command Terminal
- Open the command line in your operating system's terminal software.
- Navigate to the directory where the JAR file is located.
- Enter
java -jar TAPro.jarand the TAPro Application should launch.
Method 2: Using .bat/.sh Scripts
Create a new text file and paste the following code into the file and edit it according to the comments:
java -jar <abosute_path_to_TAPro.jar>Replace
<absolute_path_to_TAPro.jar>with the path to TAPro on your system, in quotes.Examples:
- On Windows:
java -jar "C:\Users\YOUR_USERNAME\Downloads\TAPro.jar" - On Linux:
java -jar /home/YOUR_USERNAME/Downloads/TAPro.jar - On macOS:
java -jar "/Users/YOUR_USERNAME/Downloads/TAPro.jar"
- On Windows:
Save the file as
TAPro.bat(Windows) orTAPro.sh(macOS/Linux).Change the admin settings of the script to allow it to run as a program:
- Windows: Right-click on the script and select Properties. Under General, check the box that says "Allow this file to run as a program".
- macOS/Linux: Open the Terminal and navigate to the directory where the script is located. Type
chmod +x <script_file_name>and press ENTER.
chmod +xchanges the permissions of the script on unix systems to allow it to be executed.Double-click on the script to launch TAPro.
Checking Java Version
Q: How can I check my Java version?
A: Open a command line and type java -version. If the command is not recognized, it means you do not have Java installed. You can install Java 11 using the Oracle guide here. Alternatively, you can install the OpenJDK version. For macOS users, you may wish to follow the instructions here.
Using TAPro
Q: What are the available commands in TAPro?
A: Please refer to the Command Summary for the list of available commands.
Q: Do I need an internet connection to use TAPro?
A: All of TAPro's functionality can be used offline! No internet connection is required.
Q: How do I save my data?
A: Data is saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Q: How can I remove a student's attendance for a particular week?
A: In TAPro, you can remove a student's attendance for a particular week using the unmark command! The syntax
for the unmark command is as follows:
The syntax for the unmark command is as follows:
unmark nn/NUSNET wk/WEEK
Q: Long names, phone numbers, emails and majors are truncated in the UI. Why does TAPro not make these text wrap around?
A: By international standards, telephone numbers should not exceed 15 digits. And typical names and email addresses are rarely too long, which falls outside of normal use cases. Lastly, most students will have no more than 2 majors. So under any normal use case, the fields will not contain texts long enough to be truncated. Having a single line of text for each field also ensures the UI remains clean and uncluttered.
Q: Can I add tags to a TAPro contact if I want to remember something additional, like a birthday?
A: Yes you can! In fact, you may use the TAG parameter of a contact to store any information you want. Simply
use edit with the INDEX of the student and the information you wish to add to the contact, and you should be on your way!
Tags are alphanumeric and cannot contain spaces or special characters.
Example: Using tag as a birthday for contacts
edit 1 t/12Dec
edit 2 t/25Jan
edit 3 t/1Mar
Example: Using tag as a industry interest
edit 1 t/EduTech
edit 2 t/Finance
edit 3 t/HealthTech
Adding new tag(s) will replace the existing tag(s).
Saving More Time
Q: How can I save more time when using TAPro?
A: You can use the advanced features like autocomplete and command history retrieval in TAPro! These features are designed to help you input commands faster and more efficiently.
Example: Unmarking a wrongly marked student's attendance
mark nn/E0123456 wk/6- Press the UP key to retrieve the previous command.
- Hold the LEFT key to move the cursor to the beginning of the command.
- Add a
unin front ofmarkto change the command tounmark nn/E0123456 wk/6. - Press ENTER!
Future enhancements include pressing the RIGHT key to move the cursor to the front of your input.